Today it seems obvious that a kilogram of sugar in Russia and Africa will be a kilogram of sugar. You will be surprised to learn that just 200 years ago, 1 pood weighed differently even in neighboring provinces. We have been brought to a common denominator by the international SI system, which most countries of the world operate today. But it was not always so. About the history of the introduction of measurement standards and the unified SI system - later in the article.
Why do we need standards?
The development of civilization has known many standards and standards of measures that have changed over the centuries. For example, a measure of weight in ancient Egypt is kikkar, in ancient Rome it is talent, in Russia it is a pood. And all these measures, replacing each other, required mankind to agree on common units of physical parameters that would be comparable to a single contractual unit (standard) for all.
With the development of scientific and technological progress, the need for such a unified system of standards only increased. Starting from the trade and economic sphere of activity, this system of standards has becomea necessity in all other areas - construction (drawings), industrial (for example, the unity of alloys) and even cultural (time intervals).
How the meter was determined
Almost until the end of the 17th century, length measures were different in different countries. But now the time has come when the development of science required a single measure of length - the Catholic meter.
The first standard was proposed by the British scientist and philosopher John Wilkins - to take the length of a pendulum, half the period of which is equal to one second, as a unit of length. But it quickly became clear that this value varies greatly depending on the place of measurement.
In 1790, the National Assembly in France, at the suggestion of the then Minister Talleyrand, adopted one standard of the meter, in 1791, the French Academy of Sciences already accepted as a standard of length one ten-millionth of the distance between the equator and the North Pole, measured along the Paris meridian. Agree, quite difficult.

Calm attempts continued
The prototype of the modern SI system was the metric system in France, which was proposed by the National Convention in 1795 to be developed by the leading scientists of that time. Worked on the development of length and mass standards Ch. Coulomb, J. Lagrange, P.-S. Laplace and others. There were several proposals, but the meridian was still measured. And the first meter standard was made of brass in 1975.
And yet June 22, 1799 should be considered the birthday of the unified system of measures and the prototype of the modern SI system of units. It was then that in France, platinum were madethe first standards of the meter and kilogram.
Years go by, the Gaussian absolute system of units (1832) and prefixes for multiple units of Maxwell and Thomson appear.
And in 1875, 17 states signed the Meter Convention. It approved the International Bureau of Measures and the International Committee of Measures, and the General Conference on Weights and Measures began its activities. At its first conference in 1889, the first unified metric system was adopted, based on the meter, kilogram, second.

The history of benchmarks continues
The development of electricity and optics makes its own adjustments to the concept of standards. Science does not stand still and requires new units of measurement.
In 1954, at the Tenth General Conference on Weights and Measures, six units were adopted - meter, kilogram, second, ampere, candela, degree Kelvin. In 1960, this system was named Systeme International d'Unites, and in 1960 the standard of the International System of Units, abbreviated as SI, was adopted. The Russian-language "SI" stands for International System. This is the SI measurement system that the whole world uses today. The exceptions were the USA, Nigeria, Myanmar.
Defining the SI system
It should be noted right away that this is not the only system of standards. Some branches of applied physics use other systems of units.
Today the International System of Physical Quantities SI is the most used metric system in the world. Its official detailed description is set out in"SI Brochure" (1970). Official definition "The International System of Units SI is a system of units based on the International System of Units, together with names and symbols, as well as a set of prefixes … with rules of application …".

Basic System
The principles of SI units are as follows:
- Seven basic units of physical quantities are defined. In the SI system, they cannot be derived from other quantities. These are kilogram (weight), meter (length), second (time), ampere (current), kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), candela (light intensity).
- Derived quantities from the values of the basic SI system are determined, which are obtained by mathematical operations with the basic quantities.
- Prefixes to quantities and rules for their use are defined. Prefixes mean that the unit must be divided / multiplied by an integer, which is a power of 10.
Meaning in life and science
As already mentioned, most countries in the world use SI units. Even if in ordinary life they use units traditional for the country, they are determined by converting to the SI system using fixed coefficients.
All basic units of the SI system are defined by means of physical constants or phenomena that are invariable and can be reproduced anywhere in the world with high accuracy. The only exception is the kilogram, the standard of which so far remains the only physical prototype.
MKS system of units (meter, kilogram,second) allows you to solve problems of mechanics, thermodynamics and other areas of theoretical physics and practical science.
But in some industries (for example, in electrodynamics), the SI system loses to other metric systems. That is why there are several metric systems in the world, the values of which are to some extent tied to the main standards - kilogram, meter and second.
SI units
Basic units (remember - there are seven of them) and their designations are presented in the table, but they are well known to all of us. The names of units in this system are written with a lowercase letter, and after the designation of units, a period is not put.
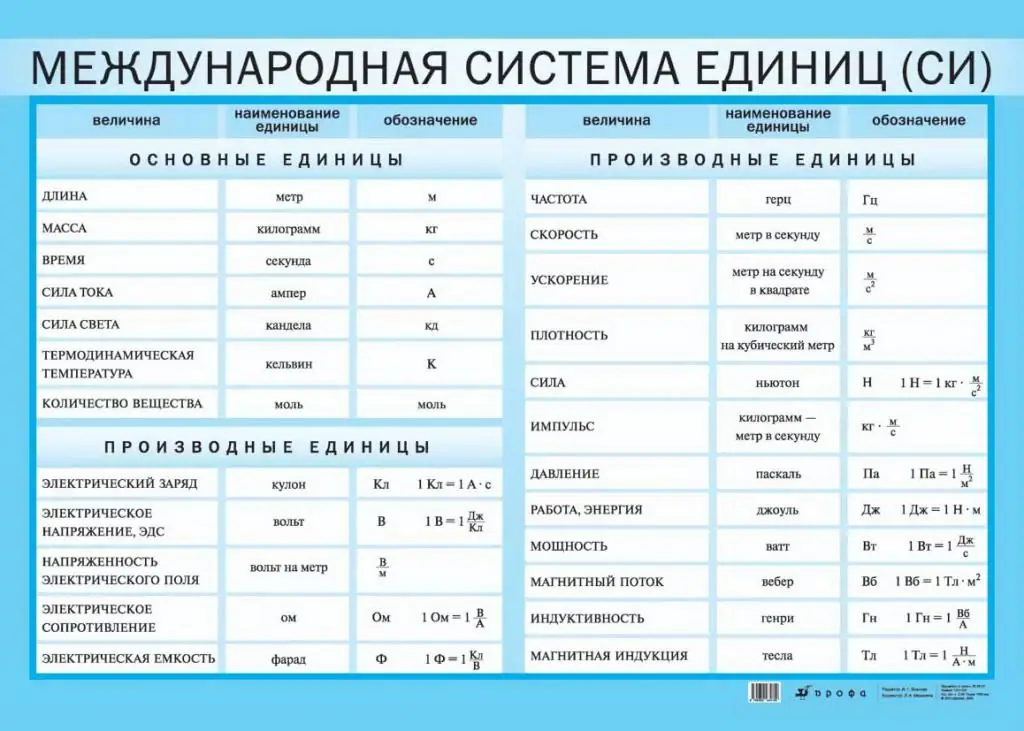
Derived units (there are 22 of them) are expressed through mathematical calculations and follow from physical laws. For example, speed is the distance that a body travels per unit of time - m / s. Some derived units have their own names (radian, hertz, newton, joule) and they can be written in different ways.
There are units that are not included in the SI system, but are allowed to be used together. They are approved by the General Convention on Weights and Measures. For example, minute, hour, day, liter, knot, hectare.
It is also allowed to use units of logarithmic values, as well as relative ones. For example, percentage, octave, decade.
The use of values that are widely used is also allowed. For example, week, year, century.
There are designed convectors for converting values from different systems. There are a lot of them, but they all rely onuniform metric values.

Advantages of the international SI system
The universality of this system is obvious. All physical phenomena, all branches of management and technology are covered by a single system of quantities. Only the SI system gives units that are important and easy to use.
The system is inherent in flexibility, which allows the use of off-system units, and the possibility of development - if necessary, the number of SI values \u200b\u200bcan be increased. Units are subject to adjustment in accordance with international agreements and the level of development of measurement technologies.
Unification of units has made this system widely used (in more than 130 countries) and recognized by many influential international organizations (UN, UNESCO, International Union of Pure and Applied Physics).
The SI system increases the productivity of designers and scientists, simplifies and facilitates the educational process and the practice of international contacts in all areas.

Last physical prototype
All units in the SI system are defined by physical constants. The exception is the kilogram. Only this standard so far has its own physical prototype and this stands out in a slender line of units of measurement.
The kilogram standard is a cylinder made of an alloy of 9 parts of platinum and 1 part of iridium. Its mass corresponds to one liter of water at its highest density (4 degrees Celsius, standard pressure above sea level). In 1889, 80 of them were made, 17 of which weretransferred to countries that signed the Metric Convention.
Today, the original of this standard under three sealed capsules is located in the city of Sevres on the outskirts of Paris in the safe of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Every year it is solemnly removed and reconciled.
The Russian version of the kilogram standard is in the All-Russian Research Institute of Metrology. Mendeleev (St. Petersburg). These are prototypes 12 and 26.

Your iPhone will break due to the loss of the mass standard in the SI system
The entire metric system of humanity is under threat today. And this happens because just the only physically existing standard is rapidly “losing weight”.
It has been experimentally proven that every century the kilogram standard becomes lighter by 3 x 10−8 kilograms. This is due to the detachment of atoms during annual surveys. It is obvious that the violation of the constant of this value will necessarily entail a change in all other values.
The Electronic Kilogram project (National Institute of Standards and Technology, USA) is called upon to save the situation, which provides for the creation of a device of such power that can lift 1 kilogram of mass in an electromagnetic field. Work on the creation is still underway.
The other direction is a cube of 2250 x 281489633 carbon-12 atoms. Its height will be 8.11 centimeters and it will not decrease over time. This project is also under development.
Interesting facts about standards and not only
Time is a constant value. InIn all time zones of our planet, time is determined relative to UTC universal time. Interestingly, this abbreviation has no decoding.
Sailors continue to use the unit "knot". Few people know, but this unit has a long history. To measure the speed of ships, a log with knots tied at the same distance was previously used. Modern speedometers have become much more perfect, but the name has been preserved.
And the measurement of motor vehicle horsepower is also based on a real fact. The inventor of the steam engine, James White, demonstrated the benefits of his discovery in this way. Under 1 horsepower, he calculated the mass of the load that the horse would lift per minute.






