Characterization of celestial bodies can be very confusing. Only stars have apparent, absolute magnitude, luminosity and other parameters. We will try to deal with the latter. What is the luminosity of stars? Does it have anything to do with their visibility in the night sky? What is the luminosity of the Sun?
Nature of stars
Stars are very massive cosmic bodies that emit light. They are formed from gases and dust, as a result of gravitational compression. Inside the stars is a dense core in which nuclear reactions take place. They make the stars shine. The main characteristics of the luminaries are the spectrum, size, brilliance, luminosity, internal structure. All these parameters depend on the mass of a particular star and its chemical composition.

The main "constructors" of these celestial bodies are helium and hydrogen. In a smaller amount relative to them, carbon, oxygen and metals (manganese, silicon, iron) may be contained. Young stars have the largest amount of hydrogen and helium, with time their proportions decrease, giving way to other elements.
Wothe inner regions of the star, the environment is very "hot". The temperature in them reaches several million kelvins. There are continuous reactions in which hydrogen is converted into helium. On the surface, the temperature is much lower and only reaches a few thousand kelvins.
What is the luminosity of stars?
Fusion reactions inside stars are accompanied by energy releases. Luminosity is also called a physical quantity that reflects exactly how much energy a celestial body produces in a certain time.
It is often confused with other parameters, such as the brightness of the stars in the night sky. However, brightness or apparent value is an approximate characteristic that is not measured in any way. It is largely related to the distance of the luminary from the Earth and describes only how well the star is visible in the sky. The smaller the number of this value, the greater its apparent brightness.

Unlike it, the luminosity of stars is an objective parameter. It does not depend on where the observer is. This is a characteristic of a star that determines its energy power. It can change in different periods of the evolution of a celestial body.
Approximate to luminosity, but not identical, is the absolute magnitude. It denotes the brightness of the star, visible to an observer at a distance of 10 parsecs or 32.62 light years. It is commonly used to calculate the luminosity of stars.
Determination of luminosity
The amount of energy that a celestial body emits is determined in watts (W), joules per second(J/s) or in ergs per second (erg/s). There are several ways to find the required parameter.
It can be easily calculated using the formula L=0, 4(Ma -M) if you know the absolute value of the desired star. So, the Latin letter L denotes luminosity, the letter M is the absolute magnitude, and Ma is the absolute magnitude of the Sun (4.83 Ma).
Another way involves more knowledge about the luminary. If we know the radius (R) and temperature (Tef) of its surface, then the luminosity can be determined by the formula L=4pR 2sT4ef. The Latin s in this case means a stable physical quantity - the Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
The luminosity of our Sun is 3.839 x 1026 Watts. For simplicity and clarity, scientists usually compare the luminosity of a cosmic body with this value. So, there are objects thousands or millions of times weaker or more powerful than the Sun.

Star luminosity classes
To compare stars with each other, astrophysicists use different classifications. They are divided according to spectra, sizes, temperatures, etc. But most often, for a more complete picture, several characteristics are used at once.
There is a central Harvard classification based on the spectra emitted by the luminaries. It uses Latin letters, each of which corresponds to a specific color of radiation (O-blue, B - white-blue, A - white, etc.).
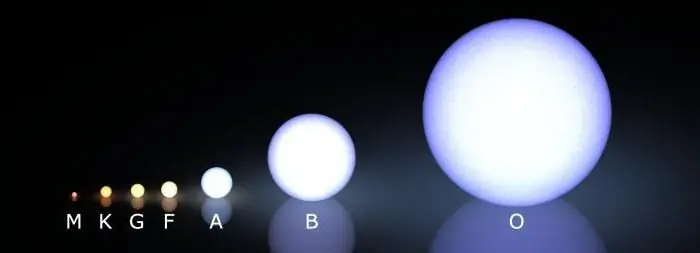
Stars of the same spectrum can have differentluminosity. Therefore, scientists have developed the Yerk classification, which also takes into account this parameter. She separates them by luminosity, based on their absolute magnitude. At the same time, each type of star is assigned not only the letters of the spectrum, but also the numbers responsible for the luminosity. So, allocate:
- hypergiants (0);
- brightest supergiants (Ia+);
- bright supergiants (Ia);
- normal supergiants (Ib);
- bright giants (II);
- normal giants (III);
- subgiants (IV);
- dwarfs of the main sequence (V);
- subdwarfs (VI);
- white dwarfs (VII);
The greater the luminosity, the smaller the value of the absolute value. For giants and supergiants, it is indicated with a minus sign.
The connection between the absolute value, temperature, spectrum, luminosity of stars is shown by the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. It was adopted in 1910. The diagram combines the Harvard and York classifications and allows you to consider and classify the luminaries more holistically.
Difference in luminosity
The parameters of the stars are strongly interconnected with each other. The luminosity is affected by the temperature of the star and its mass. And they largely depend on the chemical composition of the star. The mass of a star becomes greater, the less heavy elements it contains (heavier than hydrogen and helium).
Hypergiants and various supergiants have the largest masses. They are the most powerful and brightest stars in the universe, but at the same time, they are the rarest. Dwarfs, on the contrary, have a small mass andluminosity, but make up about 90% of all stars.
The most massive star currently known is the blue hypergiant R136a1. Its luminosity exceeds the solar one by 8.7 million times. A variable star in the constellation Cygnus (P Cygnus) surpasses the Sun in luminosity by 630,000 times, and S Doradus exceeds this parameter by 500,000 times. One of the smallest stars known, 2MASS J0523-1403 has a luminosity of 0.00126 of the Sun.






