Every person in the modern world, when planning to take out a loan or stock up on vegetables for the winter, periodically encounters such a concept as “average”. Let's find out: what it is, what types and classes of it exist, and why it is used in statistics and other disciplines.
Average - what is it?
A similar name (CB) is a generalized characteristic of a set of homogeneous phenomena, determined by any one quantitative variable.

However, people far from such abstruse definitions understand this concept as an average amount of something. For example, before taking a loan, a bank employee will definitely ask a potential client to provide data on the average income for the year, that is, the total amount of money a person earns. It is calculated by summing the earnings for the entire year and dividing by the number of months. Thus, the bank will be able to determine whether its client will be able to repay the debt on time.
Why is it used?
As a rule, averages are widely used in order togive a final description of certain social phenomena that are of a mass nature. They can also be used for smaller calculations, as in the case of a loan, in the example above.

However, most often averages are still used for global purposes. An example of one of them is the calculation of the amount of electricity consumed by citizens during one calendar month. Based on the data obtained, maximum norms are subsequently set for categories of the population that enjoy benefits from the state.
Also, with the help of average values, the warranty period of the service life of certain household appliances, cars, buildings, etc. is developed. Based on the data collected in this way, modern labor and rest standards were once developed.
In fact, any phenomenon of modern life, which is of a mass nature, in one way or another is necessarily connected with the concept under consideration.
Application areas
This phenomenon is widely used in almost all exact sciences, especially those of an experimental nature.
Finding the average value of a quantity is of great importance in medicine, engineering, cooking, economics, politics, etc.
Based on the data obtained from such generalizations, they develop medical drugs, educational programs, set minimum living wages and salaries, build study schedules, produce furniture, clothes and shoes, hygiene items and much more.
In mathematics, this term is called the "average value" and is used to implement solutions to various examples and problems. The simplest of these are addition and subtraction with ordinary fractions. After all, as you know, in order to solve such examples, it is necessary to bring both fractions to a common denominator.
Also, in the queen of the exact sciences, the term “average value of a random variable” is often used, which is close in meaning. To most, it is more familiar as "expectation", more often considered in probability theory. It is worth noting that a similar phenomenon also applies when performing statistical calculations.
Average in statistics
However, the most commonly studied concept is used in statistics. As you know, this science itself specializes in the calculation and analysis of the quantitative characteristics of mass social phenomena. Therefore, the average value in statistics is used as a specialized method for achieving its main objectives - the collection and analysis of information.

The essence of this statistical method is to replace the individual unique values of the characteristic under consideration with a certain balanced average.
An example is the famous food joke. So, at a certain factory, on Tuesdays for lunch, his bosses usually eat meat casserole, and ordinary workers eat stewed cabbage. Based on these data, we can conclude that, on average, the plant staff dines on cabbage rolls on Tuesdays.
Although this example is slightly exaggerated, howeverit illustrates the main disadvantage of the method of finding the average value - leveling the individual characteristics of objects or persons.
In statistics, average data are used not only to analyze the collected information, but also to plan and predict further actions. It also evaluates the results achieved (for example, the implementation of a plan for growing and collecting wheat harvest for the spring-summer season).
How to calculate correctly
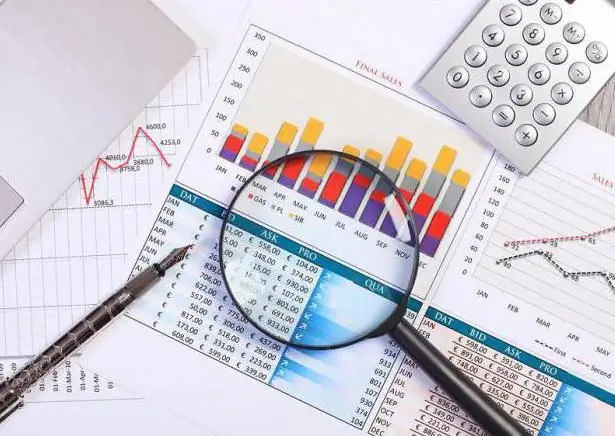
Although depending on the type of SI, there are different formulas for calculating it, in the general theory of statistics, as a rule, only one method for calculating the average value of a feature is used. To do this, you must first add together the values of all phenomena, and then divide the resulting sum by their number.
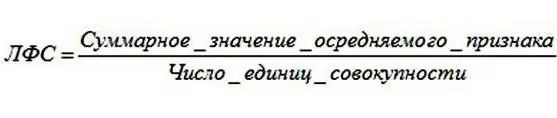
When making such calculations, it is worth remembering that the average value always has the same dimension (or units) as a separate unit of the population.
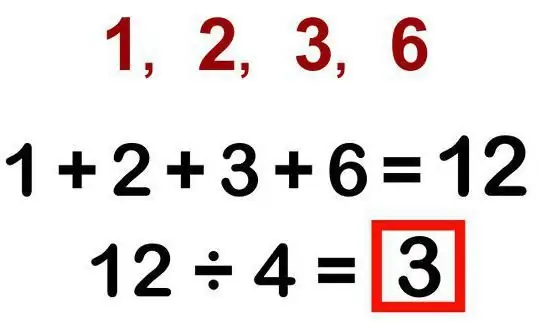
Conditions for correct calculation
The above formula is very simple and universal, so it is almost impossible to make a mistake in it. However, two aspects should always be taken into account, otherwise the data obtained will not reflect the real situation.

CB classes
Having found answers to the basic questions: "The average value - what is it?", "Where is it used?" and "How can I calculate it?", it is worth knowing what classes and types of CB exist.
First of all, this phenomenon is divided into 2 classes. These are structural and power averages.
Types of power SW
Each of the above classes, in turn, is divided into types. The power class has four.

- The arithmetic mean is the most common type of CV. It is an average term, in determining which the total volume of the considered attribute in the data set is equally distributed among all units of this set.
-
The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the simple arithmetic mean, calculated from the reciprocalsof the characteristic under consideration.
It is used in cases where the individual values of the characteristic and the product are known, but the frequency data are not.
-
The geometric mean is most often used in the analysis of growth rates of economic phenomena. It makes it possible to keep the product of individual values of a given quantity unchanged, rather than the sum.
It can also be simple and weighted.
-
Root-mean-square value is used in the calculation of individual indicators of indicators, such as the coefficient of variation, which characterizes the rhythm of output, etc.
Also, it is used to calculate the average diameters of pipes, wheels, the average sides of a square and the like figures. Like all other types of CV averages, rms can be simple and weighted.
Types of structural quantities
Besides average CVs, structural types are often used in statistics. They are better suited for calculating the relative characteristics of the values of a variable trait and the internal structure of distribution series.
There are two such species.
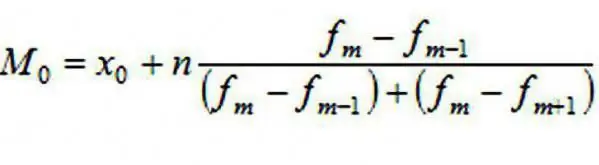
In it M0 is the value of the mode, x0 is the lower limit of the modal interval, h is the value of the considered interval, f m is its frequency, fm-1 is the frequency of the preceding modal interval andfm+1 - the next frequency.
The median is the value of the attribute that underlies the ranked series and divides it into two parts, equal in numerical terms.
In the formulas, this type is denoted as Me . Depending on which series this type of structural RV is determined (discrete or interval variational), various formulas for its calculation are used.






