At first glance, it seems that modern taxonomy has already identified all the main taxa and has no controversial issues. But that's not the case at all. Have you heard of such a systematic unit as protists? If not, then our article is for you.
Discovery history
Protists is a concept that was first introduced into science by the German naturalist Ernst Haeckel. It happened in 1886. At that time, two kingdoms of living nature were already known: Plants and Animals. The scientist classified all other living organisms as protists. However, science did not stand still. Taxonomists singled out new leading characters, created taxa. And in 1969, the American ecologist Roberg Whittaker described protists in a modern way. By the way, this scientist is called the author of the "five kingdoms" system. This classification of all living things is still relevant today.
Characteristics of protists
Protists include all organisms whose body does not form true tissues. And it does not matter how many cells they are formed. The structure of protists is characterized by the presence of a nucleus. Among the plants in this groupalgae belong. Heterotrophic protists are represented by protozoa and mushroom-like organisms.
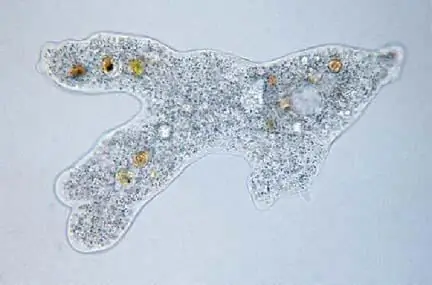
The structure of algae
Description of protists, let's start with the very first plants that appeared on the planet - algae. Among them there are unicellular representatives. These are chlamydomonas and chlorella. Despite the fact that their entire body is represented by a single cell, they carry out all life processes. This is breathing through the membrane, movement with the help of a flagellum, autotrophic nutrition, reproduction by dividing in two or spore formation. Multicellular algae are more diverse. In their body, cells are anatomically connected but do not form tissues. Such structures are called thallus, or thallus.
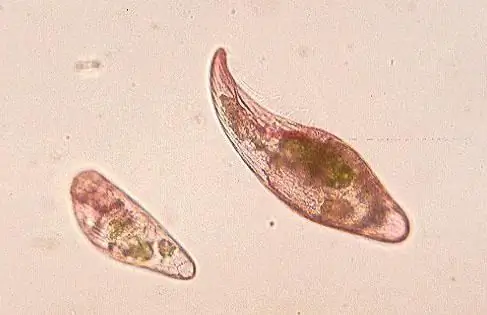
Heterotrophic protists
This group includes species that are able to feed only on ready-made organic substances. Heterotrophic protists are unicellular, or protozoan animals. Despite the name, their structure is also quite complex. One of the most common representatives of the simplest is the ciliate shoe. Like all animals, their surface apparatus is represented by a plasma membrane and a pellicle, which is a compacted layer of the cytoplasm. The permanent organelles of these protists are digestive and contractile vacuoles. The first carry out the enzymatic breakdown of organic substances, and the second - the regulation of osmotic pressure and water-s alt metabolism.
Ciliates even havesexual process, which is carried out in the form of conjugation. At the same time, two animals approach each other, a cytoplasmic bridge is formed between them, along which the nuclei exchange genetic information. The organelles of the movement of heterotrophic protists are very diverse. In ciliates, these are numerous cilia, in euglena - a single flagellum. But the amoeba Proteus forms non-permanent protrusions of the cytoplasm, which are called pseudopodia, or pseudopodia.
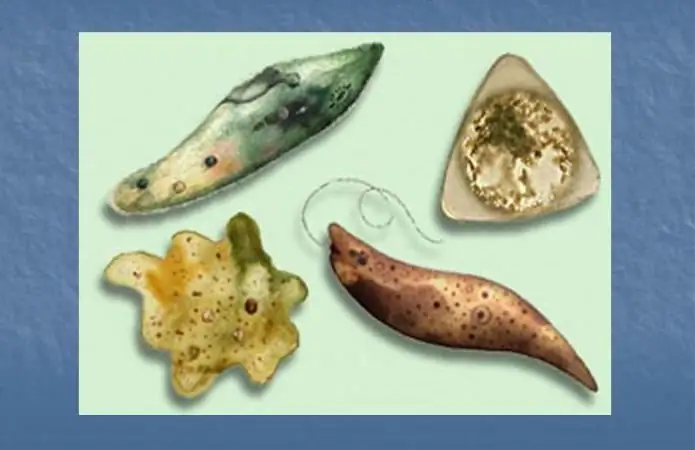

Mushroom-like protists
This group of protists resembles real mushrooms vaguely. For example, the body of labyrinthules is represented by reticulated wandering plasmodia. And the cell wall of oomycetes consists of rigid cellulose. In addition, in the process of asexual reproduction, they form mobile zoospores. These features are also characteristic of half the order of Hyphochytridia, most of which are intracellular parasites of algae and invertebrates.
Unique Features
Protists are organisms that have very unusual characteristics. These include the pseudopodia of mushroom-like labyrinthules. They merge with similar structures of neighboring cells, forming a whole network. Representatives of the chrysophyte order are equipped with a special outgrowth called a haptonema. It consists of microtubules surrounded by a canal of the endoplasmic reticulum. Dinophyte algae have a nuclear structure inherent only to them, the chromosomes in which are always in a spiralized state.
What is polyphilia
Very often, protists are called polyphyleticgroup or taxon. This means that its composition includes organisms that have proven kinship with representatives of other systematic units that are not included in this one. So, protozoa belong to the animal kingdom, and algae belong to the plant kingdom. Polyphyletic taxa are not part of modern taxonomy, since their representatives do not have a common ancestor. Examples of such groups are cold-blooded animals or autotrophic bacteria.
So, protists are eukaryotic organisms that do not form true tissues. Among them there are unicellular and multicellular species, auto- and heterotrophs. Modern representatives of protists include algae, protozoa and mushroom-like organisms.






