The North Atlantic Alliance (NATO) on the way of its development has undergone several stages of expansion and repeated changes in the concept of activity. The problem of NATO expansion became acute for Russia as the organization moved to the East, to the borders of the Russian Federation.

Historical background to the creation of NATO
The need to create various kinds of alliances appeared on the fragments of the old world after the Second World War. Post-war reconstruction, assistance to the affected countries, improvement of the welfare of the member states of the union, development of cooperation, ensuring peace and security - all this became the main reasons for the intensification of integration processes in Europe.
The contours of the UN were outlined in 1945, the Western European Union became the forerunner of the modern EU, the Council of Europe - the same age as NATO - was formed in 1949. The ideas of European unification were in the air since the 20s of the twentieth century, but until the end of a large-scale war there was no way to form an alliance. Yes, and the first attempts at integration were also not crowned with particular success: organizations created in the first post-war years, duringwere in many ways fragmented and short-lived.
Starting point of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization or North Atlantic Alliance) was founded in 1949. The main tasks of the military-political union were declared to be the preservation of peace, the provision of assistance to the affected states and the development of cooperation. Hidden motives for the creation of NATO - opposition to the influence of the USSR in Europe.

12 states became the first members of the North Atlantic Alliance. To date, NATO has already united 28 countries. The organization's military spending accounts for 70% of the global budget.
NATO Global Agenda: Thesis on the goals of the military alliance
The main purpose of the organization of the North Atlantic Treaty, enshrined in the said document, is the preservation and maintenance of peace and security in Europe and other countries - members of the Union (USA and Canada). Initially, the block was formed to contain the influence of the USSR, by 2015 NATO came to a modified concept - the main threat is now considered a possible attack by Russia.
The intermediate stage (beginning of the 21st century) provided for the introduction of crisis management, the expansion of the European Union. NATO's Global Program "Active Participation, Modern Defense" then became the organization's main instrument in the international arena. Currently, security is maintained mainly through the deployment of military facilities on the territory of the participating countries and the presence of NATO military contingents.
Main stages of expansionmilitary alliance
NATO expansion is briefly contained in several stages. The first three waves occurred even before the collapse of the Soviet Union, in 1952, 1955 and 1982. Further NATO expansion was characterized by rather aggressive actions against Russia and advance into Eastern Europe. The largest expansion took place in 2004, at the moment eight states are candidates for joining the North Atlantic Alliance. All these are countries of Eastern Europe, the Balkan Peninsula and even Transcaucasia.
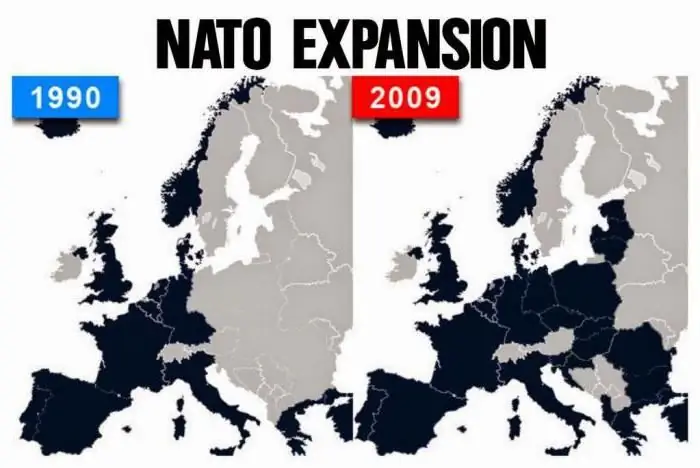
The reasons for NATO expansion are clear. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization is spreading its influence and strengthening its presence in Eastern Europe in order to suppress the imaginary Russian aggression.
First wave of expansion: Greece and Turkey
The first expansion of NATO included Greece and Turkey in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. The number of member countries of the military bloc first increased in February 1952. Later, Greece did not participate in NATO for some time (1974-1980) due to tense relations with Turkey.
West Germany, Spain and failed member of the union
The second and third expansion of NATO was marked by the accession of Germany (from the beginning of October 1990 - united Germany) exactly ten years after the legendary Victory Parade and Spain (in 1982). Spain will later withdraw from the military bodies of NATO, but will remain a member of the organization.
In 1954, the alliance offered to join the North Atlantic Treaty and the Soviet Union,however, the USSR, as expected, refused.
Accession of the Visegrad Group countries
The first really tangible blow was the expansion of NATO to the East in 1999. Then three of the four states of the Visegrad Four, which united several countries of Eastern Europe in 1991, joined the alliance. Poland, Hungary and the Czech Republic joined the North Atlantic Treaty.
The Biggest Expansion: Road to the East
The fifth expansion of NATO included seven states of Eastern and Northern Europe: Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, Bulgaria and Slovenia. A little later, the US Secretary of Defense said that Russia was "on the threshold of NATO." This once again provoked the strengthening of the alliance's presence in the states of Eastern Europe and responded with a change in the concept of the organization of the North American Treaty in the direction of protection against possible Russian aggression.

Expansion Phase Six: A Clear Threat
The latest expansion of the North Atlantic Alliance took place in 2009. Then Albania and Croatia, located on the Balkan Peninsula, joined NATO.
NATO Membership Criteria: List of Commitments
Not any state that has expressed a desire to become a member of the North Atlantic Alliance can join NATO. The organization puts forward a number of requirements for potential participants. Among these membership criteria are the fundamental requirements adopted in 1949:
- location of a potential NATO member inEurope;
- consent of all members of the alliance to join the state.
There have already been precedents with the last point. Greece, for example, is preventing Macedonia from joining the North Atlantic Treaty Organization for the reason that the conflict over the name of Macedonia has not yet been resolved.
In 1999, the list of obligations of NATO members was supplemented with several more items. Now a potential member of the alliance must:
- resolve international disputes exclusively by peaceful means;
- solving ethnic, intrastate, territorial and political disputes in accordance with OSCE principles;
- respect human rights and the rule of law;
- organize control over the armed forces of the state;
- if necessary, freely provide information about the economic state of the country;
- take part in NATO missions.

What's interesting: the list of obligations is somewhat incorrect, as it includes non-fulfillment of some items. Ignoring certain points by a potential member of the alliance affects the final decision on admission to NATO, but is not critical.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization Partnership Programs
The military alliance has developed several cooperation programs that facilitate the entry of other states into NATO and provide a wide geography of influence. Mainprograms are as follows:
- "Partnership for Peace". To date, 22 states are participating in the program, there are thirteen former participants: 12 of them are already full members of the alliance, Russia, the remaining former participant in the partnership program, withdrew from the PfP in 2008. The only EU member that does not participate in the PfP is Cyprus. Turkey is preventing the state from joining NATO, citing the unresolved conflict between the Turkish and Greek parts of Cyprus.
- Individual affiliate plan. Eight States are currently members.
- "Fast Dialogue". Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Ukraine, Georgia participate in it.
- Membership action plan. It was developed for three states, two of which were previously participants in the Accelerated Dialogue program: Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Macedonia has also been participating in the program since 1999.
Seventh wave of expansion: who will join NATO next?
Partnership programs suggest which states will become the next members of the alliance. However, it is impossible to speak unambiguously about the timing of joining the ranks of the participants in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. For example, Macedonia has been conducting an accelerated dialogue with NATO since 1999. While ten years have passed from the moment of signing the PfP program to the direct entry into the ranks of the member states of the alliance for Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia, for Hungary, Poland and the Czech Republic -only five, for Albania - 15.

Partnership for Peace: NATO and Russia
NATO expansion contributed to increased tensions regarding the future actions of the alliance. The Russian Federation participated in the Partnership for Peace program, but further conflicts regarding the expansion of NATO to the East, even if Russia was against it, left no choice. The Russian Federation was forced to end its participation in the program and start developing response measures.
Since 1996, Russia's national interests have become more concrete and clearly defined, but the problem of NATO expansion to the East has become more acute. At the same time, Moscow began to put forward the idea that the main guarantor of security in Europe should be not a military bloc, but the OSCE - the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe. A new stage in relations between Moscow and NATO was legally fixed in 2002, when the declaration “Russia-NATO Relations: A New Quality” was signed in Rome.
Despite a brief easing of tensions, Moscow's negative attitude towards the military alliance only deepened. The instability of relations between Russia and the North Atlantic Alliance continues to be demonstrated during the organization's military operations in Libya (in 2011) and Syria.
Conflict issue
NATO expansion to the East (briefly: the process has been going on since 1999, when Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary joined the alliance, and still) -this is a serious reason for the exhaustion of the credibility of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. The fact is that the problem of strengthening its presence near the borders of Russia is exacerbated by the question of the existence of agreements on the non-expansion of NATO to the East.
During the negotiations between the USSR and the USA, an agreement was allegedly reached on the non-expansion of NATO to the East. Opinions differ on this issue. Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev spoke verbally about receiving guarantees that NATO would not expand to the borders of modern Russia, while representatives of the alliance claim that no promise was made.
Much of the disagreement over the non-expansion promise was due to a misinterpretation of the German Foreign Minister's 1990 speech. He urged the alliance to declare that there would be no advance to the borders of the Soviet Union. But are such assurances a form of promise? This dispute has not yet been resolved. But the confirmation of the promise of non-expansion of the alliance to the East could become a trump card in the hands of the Russian Federation in the international arena.






