Acceleration and speed are two important kinematic characteristics of any type of movement. Knowing the dependence of these quantities on time allows you to calculate the path traveled by the body. This article contains the answer to the question of how to find the acceleration, knowing the speed and time.
The concept of speed and acceleration
Before giving an answer to the question of how, knowing speed and time, to find acceleration, let's consider each of the characteristics from the point of view of physics.
Speed is a value that determines the speed of change of coordinates in space when the body moves. The speed is calculated by the formula:
v=dl/dt.
Where dl is the path traveled by the body during the time dt. The speed is always directed along the tangent in the motion path.
Movement can occur either at a constant speed over time, or at a variable speed. In the latter case, we speak of the presence of acceleration. In physics, acceleration determines the rate of change of v, which is written as a formula:
a=dv/dt.
This equality is the answer to the question of how to findspeed acceleration. To do this, it is enough just to take the first time derivative of v.
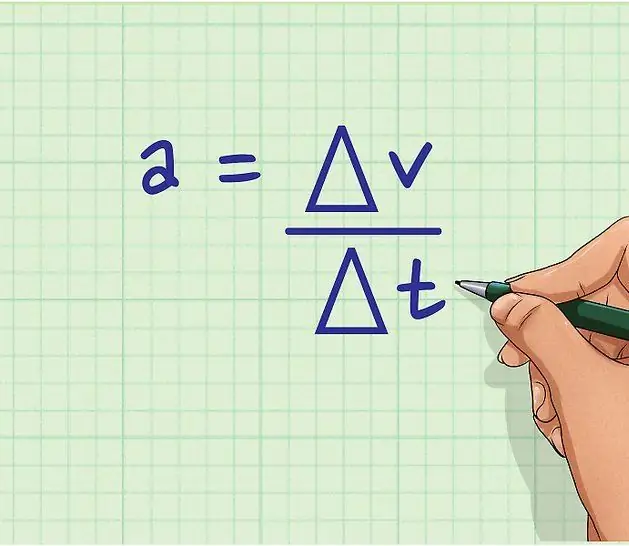
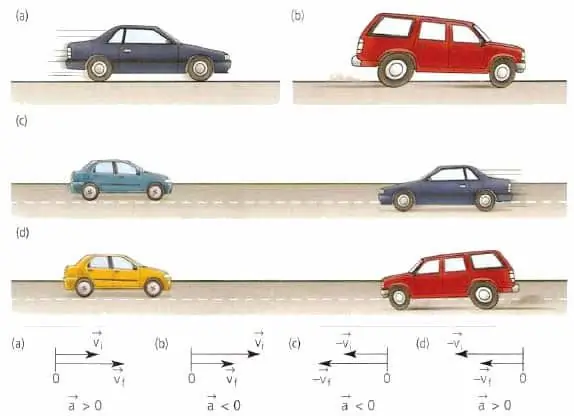
The direction of acceleration coincides with the direction of the difference in the velocity vectors. In the case of rectilinear accelerated motion, the quantities a and v are directed in the same direction.
How to find acceleration given speed and time?
When studying mechanics, one first considers uniform and uniformly accelerated types of motion along a straight trajectory. In both cases, the time interval Δt should be chosen to determine the acceleration. Then, it is necessary to determine the speed values v1 and v2 at the ends of this interval. Average acceleration is defined as follows:
a=(v2- v1)/Δt.
In the case of uniform motion, the speed remains constant (v2=v1), so the value of a will be zero. In the case of uniformly accelerated movement, the value a will be constant, so it does not depend on the time interval Δt in the formula.
For more complex cases of movement, when the speed is a function of time, you should use the formula for a through the derivative, which was presented in the paragraph above.
Example of problem solving
Having de alt with the question of how to find the acceleration, knowing the time and speed, we will solve a simple problem. Suppose that the body, moving along a certain trajectory, changes its speed in accordance with the following equation:
v=3t2- t + 4.
What will be the acceleration of the body at time t=5 seconds?
The acceleration is the first derivative of v with respect to the variable t, we have:
a=dv/dt=6t - 1.
To answer the question of the problem, you should substitute the known value of time into the resulting equation: a=29 m/c2.






